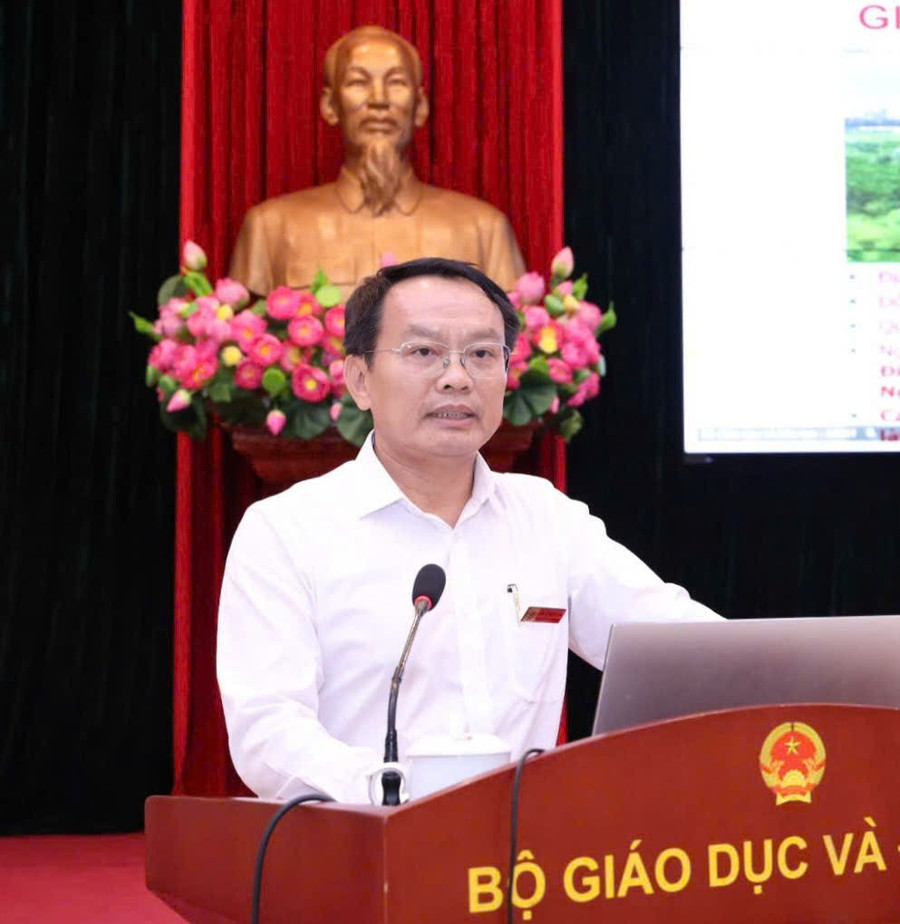
Associate Professor, Dr. Pham Xuan Khanh - Principal of Hanoi College of Technology, shared analysis of development trends, impacts of the new context and proposed breakthrough solutions to improve the quality of vocational education .
Development trends
- According to you, what will the development trend of vocational education in the period 2025 - 2030 focus on?
- According to the World Economic Forum, the top skills needed for workers in the period 2024 - 2030 are: Analytical and creative thinking; proactive learning strategies; solving complex problems; critical thinking. These skills are different from "hard" skills, such as accuracy, endurance, memory, financial management, resources... which were important for workers in the recent period. Up to now, vocational education has not met the above-mentioned needs for human resources with new skills and higher qualifications, posing an increasingly greater challenge to the labor market.
Therefore, the trend of vocational education development in the period 2025 - 2030 is to rapidly increase the scale of training, while improving quality - an urgent requirement. In particular, the vocational education system has developed strongly, formed in an open, interconnected direction, basically in line with countries around the world . Conditions to ensure training quality have been strengthened, initially forming a number of high-quality training facilities and training programs according to international standards.
The rate of workers with vocational training and degrees and certificates; the rate of workers with jobs suitable to their vocational skills and training level has increased; Vietnamese workers have gradually participated and taken on many job positions previously held by foreign experts. At the same time, attracting FDI capital has shifted strongly to Vietnam in the context of diversifying the global supply chain, contributing to socio-economic development, industrialization and modernization of the country.

New opportunities and challenges
- With the above trend, in the current context, what opportunities and challenges does Vietnamese vocational education face, sir?
- First of all, opportunities and challenges from within the labor market. Vietnam has an abundant labor supply, high adaptability, and is considered to quickly absorb advances in science and technology in production and management skills. The labor structure is shifting in a positive direction. The proportion of people of working age participating in the labor force remains high; the unemployment rate is low compared to the region, only approximately 2%. The quality of jobs and income of workers have steadily increased. The level of discrimination between pay for male and female workers has narrowed. The number of workers working abroad under contracts continues to increase.
However, the labor market still has many limitations. Laborers mainly work in the agricultural sector, which is unstructured, low-productivity, and risky. There is a surplus of labor in agriculture and rural areas with low quality labor supply, and unskilled labor accounts for a large proportion.
The unemployment rate is still quite serious and the number of unsustainable jobs accounts for a large proportion. The ability to connect labor supply and demand is not good; there is a serious imbalance between labor supply and demand. Some industries, occupations, and localities cannot recruit workers; there is a lack of appropriate policies to manage domestic and international labor migration.
Second, opportunities and challenges from economic integration and opening the labor market. Vietnam is increasingly integrating more deeply into the global economy. Therefore, forms of international cooperation in vocational education are identified. Free labor movement within the ASEAN bloc is increasingly developing, workers from other countries have the right to enter Vietnam to work and vice versa. This is also considered a labor trend in the coming years.
According to the forecast of the International Labor Organization (ILO), when joining AEC, the number of jobs in Vietnam will increase by 14.5% by 2030; the abundant labor market, the increasing demand for skilled labor is a great opportunity for Vietnam. However, the quality of human resources in Vietnam is still lower than that of other countries in the region. Low labor productivity, lack of skilled labor, foreign language proficiency and other soft skills are making Vietnamese workers weak in the fierce competition when integrating. The possibility of surplus low-skilled labor, job loss right at home is starting to happen.
Third, in the fourth industrial revolution, creative industries are growing strongly, accounting for an increasingly high proportion in the economic structure compared to traditional manufacturing and service industries. This requires the labor structure by industry to change accordingly to meet new human resource needs.
With the application of technological achievements, many industrial fields are automated to replace humans, the requirements for workers' skills will be increasingly high. According to forecasts, by 2030, up to 80% of new jobs will be unprecedented in the present time; thus, it can put enormous pressure on training human resources to meet market needs...
Breakthrough solutions to improve quality
- To meet human resource requirements in the new context, what do you think are the important groups of solutions that need to be prioritized for implementation?
- I think it is necessary to synchronously implement solutions on: Management organization; synchronous investment from area, factory to training equipment; accelerate digital transformation; innovate enrollment and training work associated with job creation; closely link vocational education with businesses, mobilize the participation and contribution of businesses in training activities; promote research, application of science and technology transfer; diversify international cooperation in vocational education.
Regarding management organization, it is necessary to review, arrange and upgrade public colleges and intermediate schools in the direction of each school being a high-quality training center linked to the socio-economic development needs of the region, area and locality. Innovate and improve the school organizational structure in a flexible and streamlined direction, arrange and assign staff according to job descriptions.
At the same time, focus on training and developing highly qualified human resources, improving the capacity and qualifications of teachers and managers, especially for new and high-tech occupations. Organize many training courses at home and abroad on new science and technology, innovation, and digital transformation for cadres and lecturers with research and production capacity in vocational education institutions. Thereby, improving professional qualifications, expertise, knowledge and skills; helping the team to have the capacity to research, apply, absorb, master and develop advanced and modern technologies, gradually forming a force of highly qualified science and technology experts. People are the key factor of success and need to be given top priority.
At the same time, improve mechanisms and policies; enhance the effectiveness of state management of vocational education. Enhance the autonomous operation capacity of schools, promote the development of policies to support the work of streaming junior high and high school students into vocational training to achieve the goals of Directive No. 21/CT-TW; support tuition fees for high school graduates to study vocational training to improve the quality of input to intermediate and college levels and other policies for the field of vocational education.
Innovation in recruitment and training associated with job creation is the number one important task in the activities of vocational training institutions. Accordingly, investment and research to open new industries and professions in the direction of high technology, spearhead industry 4.0 such as: AI, mechanical engineering, semiconductor technology, biotechnology, smart energy, Robots, Logistics, high-tech agriculture...
Vocational training institutions need to innovate teaching and learning methods and organize them in an open, cumulative, and recognition-based way, creating the most favorable conditions for learners to learn continuously and learn for life. Deploy a school management system in the direction of thinking and technology, autonomy, self-responsibility, ensuring creativity and quick adaptation to the constant innovation and development of science and technology. Teaching and learning shift to ideas, creativity and technology application; apply simulation software, build virtual practice lectures, and cooperate with businesses to organize training at businesses.
Regularly updating changes in technology and science in a timely manner to incorporate them into training programs that are appropriate to the new context is also an important requirement. Gradually applying advanced programs taught in foreign languages; adding modules on innovative entrepreneurship skills, digital skills, etc. to the training program.
In addition, innovate training programs based on output standards. Ensure smooth connection between training levels within the same industry or profession; or with other industries or professions; or connection to higher levels in the national education system.
Thank you very much!
To realize the Party and State's policies on innovation and development of vocational education, in addition to the leadership, direction and investment of the State, ministries, branches, localities and vocational education institutions need to proactively innovate from mechanisms and policies to the entire training organization process. Vocational education institutions need to absorb and apply new scientific and technological knowledge of the world, the advantages of modern vocational training models to create a breakthrough in education quality.
Source: https://giaoducthoidai.vn/doi-moi-giao-duc-nghe-nghiep-don-co-hoi-vuot-thach-thuc-post759541.html




![[Photo] 60th Anniversary of the Founding of the Vietnam Association of Photographic Artists](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F05%2F1764935864512_a1-bnd-0841-9740-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)


![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attends the VinFuture 2025 Award Ceremony](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F05%2F1764951162416_2628509768338816493-6995-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)




































































































Comment (0)