Some higher education institutions offer college and vocational training programs.
The Law on Vocational Education consists of 9 chapters and 46 articles, and will come into effect on January 1, 2026.
The law regulates vocational education activities within the national education system; the organization and operation of vocational education institutions; the rights and responsibilities of organizations and individuals participating in vocational education activities; and state management of vocational education.
The law stipulates the development of the vocational education system in an open, flexible, diverse, and interconnected manner, ensuring standardization, modernization, socialization, and international integration; with a focus on high-quality vocational education.
.jpg)
Vocational education budgets are prioritized within the total state budget allocated to education and training, aiming to standardize vocational education institutions; modernize a number of key, high-quality colleges to meet international standards, in line with the development of priority industries and professions in major economic centers.
At the same time, the aim is to train highly skilled human resources in technical and technological fields; national key industries; industries that are on par with advanced regional and international standards; and national strategic and key programs and projects; and to develop vocational education in areas with particularly difficult socio-economic conditions, ethnic minority regions, mountainous areas, border areas, islands, and coastal areas.

To determine the position of vocational secondary education within the National Qualifications Framework's level/qualification system, the Law stipulates that vocational secondary education programs aim to complete general education while equipping learners with the capacity to perform and solve tasks in stable conditions and familiar environments of their respective industries and professions; enabling them to apply modern techniques and technologies to their work, work independently, and work in teams.
Students who complete the vocational secondary education program and meet the prescribed requirements are eligible to take the graduation exam; if they pass, they will be awarded a vocational secondary education diploma by the head of the vocational education institution; in cases where students do not take the graduation exam or fail, they will be issued a certificate of program completion by the head of the vocational education institution.
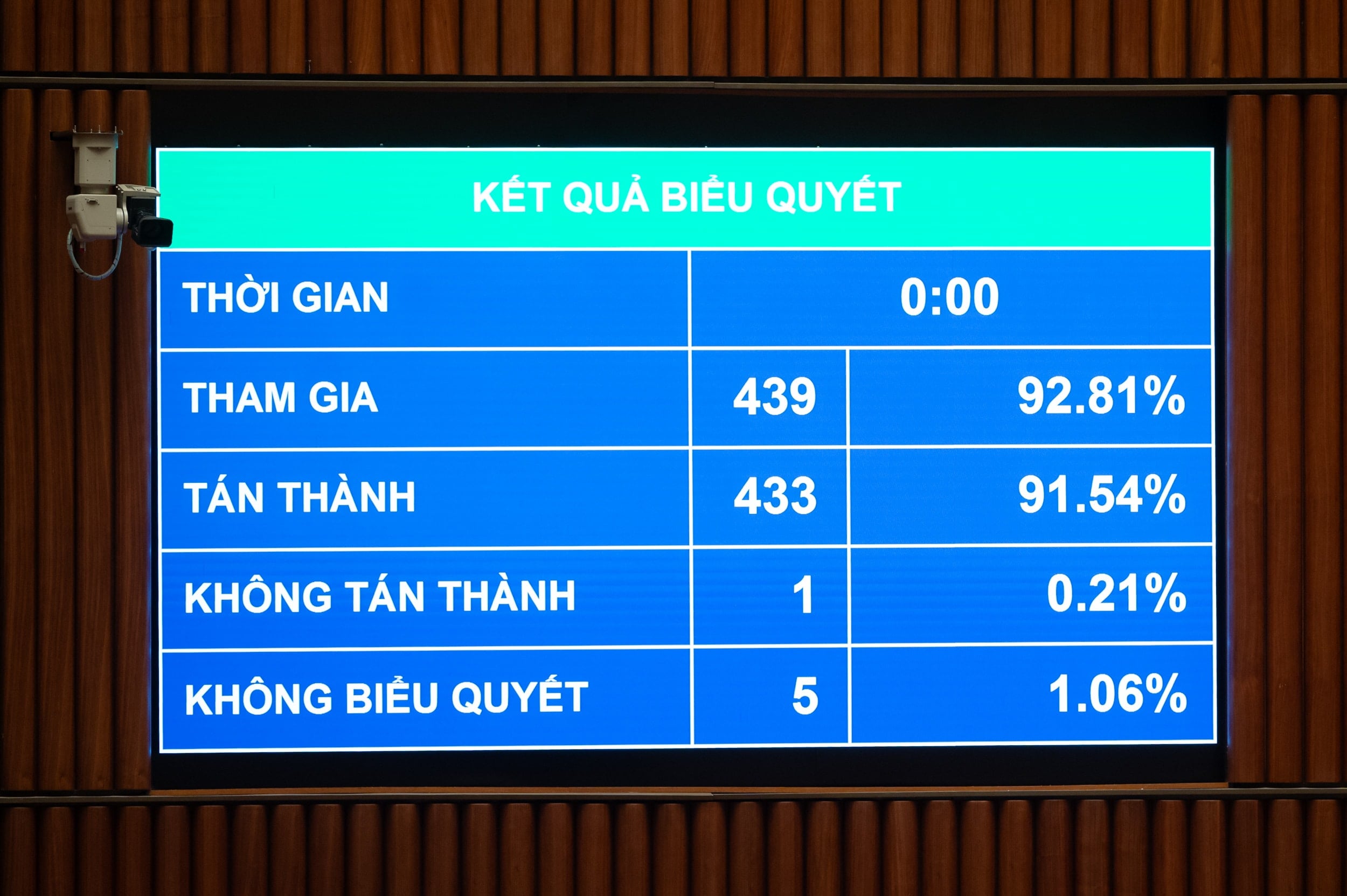
Regarding vocational education institutions, the Law stipulates that these institutions include colleges, vocational secondary schools, and vocational high schools; their mission is to train skilled human resources at various levels of vocational education for the socio-economic development of the country.
In addition, higher education institutions that are training students in specialized fields or groups of fields in the arts and sports at the university level; training students in teacher training programs at the university level; institutions of the People's Armed Forces; and institutions that are training students in fields listed in the Strategic Technology Catalogue according to the Prime Minister's Decision at the university level will be allowed to implement college-level training programs in the same fields.
Specifically, clarify the policy of prioritizing businesses participating in vocational training.
Earlier, Minister of Education and Training Nguyen Kim Son reported on the process of receiving feedback, providing explanations, and revising the draft Law on Vocational Education (amended).
Accordingly, in line with the directives of the Party, the National Assembly, and the Government, the drafting committee of the revised Law on Vocational Education has conducted practical research, consulted international experiences, and promptly institutionalized the Resolutions of the Party, the National Assembly, and the Government to finalize the draft for submission to the National Assembly with many new points.
Firstly, the national education system should be perfected towards openness, flexibility, and interconnectedness, creating lifelong learning opportunities for all citizens through the addition of vocational high school models and the expansion of the target group participating in vocational education activities. Vocational high schools are defined as being at the same level as high schools, integrating core knowledge from the high school curriculum with vocational skills to help learners complete their general education.

The addition of vocational high school models aims to strengthen career guidance for young people right from the secondary school level, increasing the number of students who enroll in vocational education after completing lower and upper secondary education.
This contributes to accelerating the roadmap for vocational training for young people in accordance with the spirit of Conclusion No. 91-KL/TW of the Politburo, continuing to implement Resolution No. 29-NQ/TW on fundamental and comprehensive reform of education and training; meeting the requirements of industrialization and modernization in the context of a socialist-oriented market economy and international integration; and overcoming limitations and weaknesses in career guidance, streaming, and articulation.
Secondly, breakthroughs in curriculum innovation, training organization, and quality assurance in vocational education are achieved through the regulation of program and training institution standards; management of registration activities on a digital data platform; and recognition of accumulated knowledge or skills of learners to participate in other learning programs.

Thirdly , strengthen the connection between vocational education institutions and businesses by specifying preferential policies for businesses and regulating the mechanism for establishing a Human Resource Training Fund for businesses. Adding regulations on a Human Resource Training Fund for businesses will be an incentive for employees to stay with businesses long-term, demonstrating a genuine commitment between businesses and schools.
Fourth, promote decentralization and delegation of power, improve the efficiency of state management in vocational education, and ensure the serious, synchronized, and stable implementation of the Party and State's directives on reviewing and reorganizing public service units and the two-tiered local government model by maximizing autonomy for vocational education institutions.
Source: https://daibieunhandan.vn/phat-trien-he-thong-giao-duc-nghe-nghiep-theo-huong-mo-da-dang-lien-thong-10399933.html






![[Photo] Explore the US Navy's USS Robert Smalls warship](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F10%2F1765341533272_11212121-8303-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)

































![[Video] The craft of making Dong Ho folk paintings has been inscribed by UNESCO on the List of Crafts in Need of Urgent Safeguarding.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/10/1765350246533_tranh-dong-ho-734-jpg.webp)








































































Comment (0)