Prioritize the application of AI in management, administration, and public service delivery.
The Law on Artificial Intelligence comprises 8 Chapters and 35 Articles, regulating the research, development, provision, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence systems (AI activities); the rights and obligations of relevant organizations and individuals; and state management of artificial intelligence (AI) activities in Vietnam.
AI activities that serve only the purposes of national defense, security, and cryptography are not within the scope of this Law.

The law stipulates that the State has a policy to develop AI to become an important driving force for growth, innovation, and sustainable development of the country. It encourages controlled technology testing; applies management measures commensurate with the level of risk; and encourages voluntary compliance mechanisms.
There are policies to ensure the rights and facilitate access to, learning from, and benefiting from AI for organizations and individuals; to encourage the development and application of AI to serve social welfare, support people with disabilities, the poor, and ethnic minorities to narrow the digital divide; and to preserve, promote, and maintain national cultural identity.
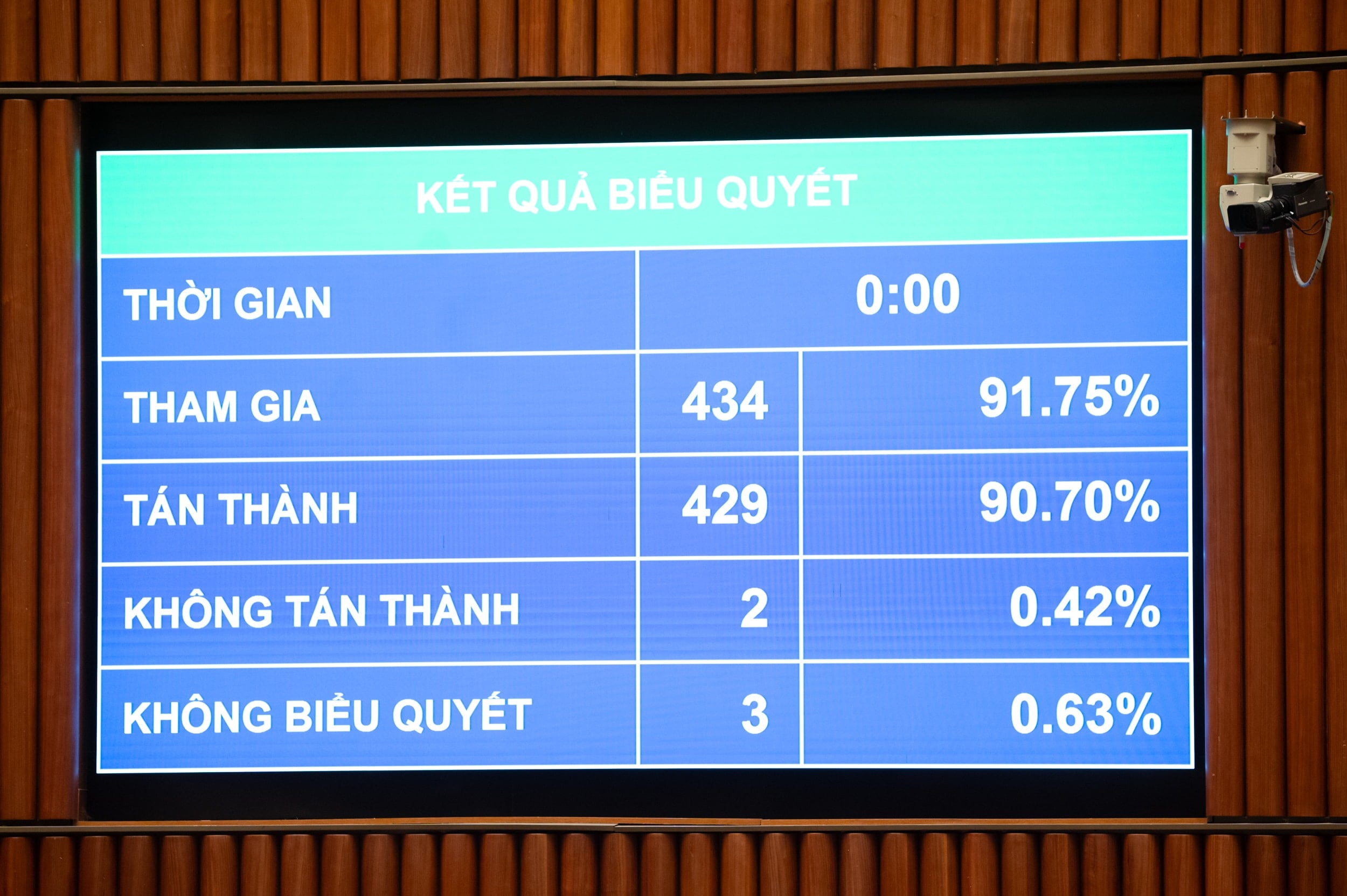
Prioritize investment and mobilize social resources to develop data infrastructure, computing infrastructure, secure AI, high-quality human resources, and shared AI platforms as part of a national strategic plan.
Prioritize the application of AI in management, administration, public service delivery, and decision-making support of state agencies to improve efficiency, transparency, and quality of service to citizens and businesses, and encourage widespread application in socio -economic sectors to enhance productivity, service quality, and management efficiency…
AI systems are categorized into high-risk, medium-risk, and low-risk levels.
Regarding the classification of AI system risk levels (Article 9), the Law stipulates that AI systems are classified according to the following levels:
A high-risk AI system is one that can cause significant harm to the lives, health, legitimate rights and interests of organizations and individuals, national interests, public interests, and national security.
A medium-risk AI system is one that has the potential to confuse, influence, or manipulate users because they are unable to recognize that the interacting entity is the AI system or the content it generates.

Low-risk AI systems are those that do not fall under the cases specified in points a and b of Clause 1 of this Article.
The risk classification of AI systems is determined based on criteria such as the level of impact on human rights, safety, and security; the system's area of use, especially in essential areas or those directly related to the public interest; the scope of users; and the scale of the system's impact.

The law also stipulates that the national AI infrastructure is a strategic infrastructure, including infrastructure invested in by the State, businesses, and social organizations; it should be developed as a unified, open, secure ecosystem capable of connectivity, sharing, and expansion, ensuring it meets the requirements for AI development and application.
The State plays a guiding, coordinating, and ensuring role in infrastructure capacity for national AI development; encourages businesses, research institutes, universities, and social organizations to invest in, build, and share infrastructure; and strengthens public-private cooperation in AI infrastructure development…
The law will come into effect on March 1, 2026.
Source: https://daibieunhandan.vn/quoc-hoi-thong-qua-luat-tri-tue-nhan-tao-10399959.html



![[Photo] The captivating scenery of the fragrant maple forest in Quang Tri](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F10%2F1765353233198_lan09046-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Photo] Explore the US Navy's USS Robert Smalls warship](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F10%2F1765341533272_11212121-8303-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)





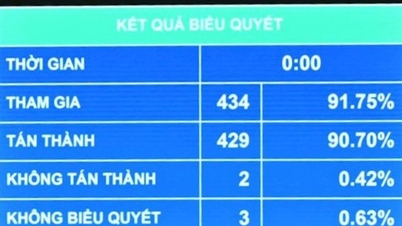









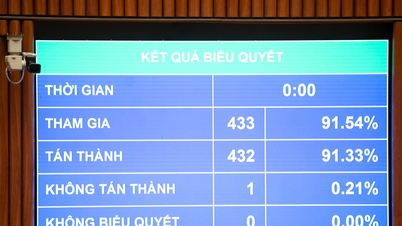












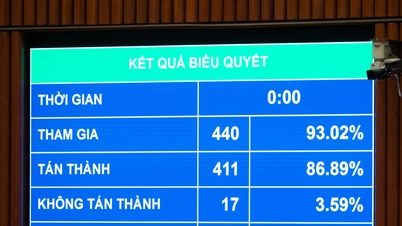







![[Video] The craft of making Dong Ho folk paintings has been inscribed by UNESCO on the List of Crafts in Need of Urgent Safeguarding.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/10/1765350246533_tranh-dong-ho-734-jpg.webp)








































































Comment (0)