Based on medical research and analysis, consuming too much protein can lead to the following harmful effects:
Eating too much protein puts a strain on the kidneys.
One of the long-term negative effects of excessive protein intake is putting strain on the kidneys. High protein consumption promotes increased glomerular filtration and can rapidly impair kidney function if left unchecked, according to the American website Eating Well .
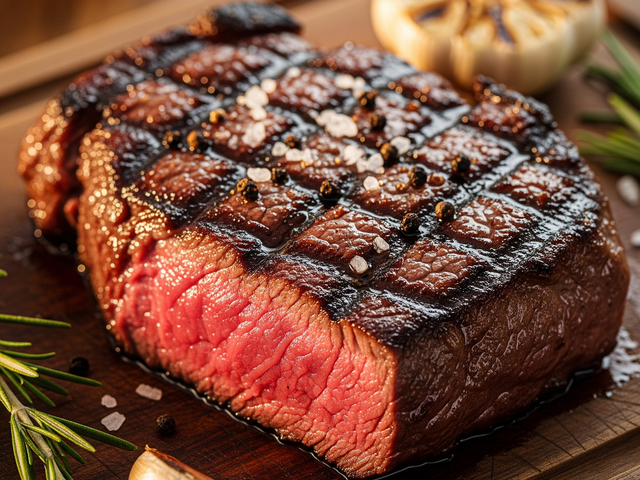

Red meat is rich in protein, but eating too much of it can cause some side effects on the body.
PHOTO: AI
When the kidneys have to work harder to remove byproducts of protein breakdown, such as urea and ammonia, it can easily lead to long-term structural damage to the kidneys. This is especially important for people with underlying kidney problems, such as those with diabetes or obesity.
Burden on the liver
After protein is broken down, it leaves behind nitrogen byproducts, which are then converted into urea or ammonia and excreted through the kidneys. However, the liver also participates in this cycle. When the amount of protein is too high, the liver has to work harder. When liver or kidney function is impaired, even mildly, processing the excess nitrogen can cause fatigue, bloating, and sometimes affect liver enzymes.
Digestive disorders
The amount of food we eat each day is limited. Therefore, prioritizing protein intake from meat and eggs will reduce the consumption of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, and mushrooms. This can easily lead to constipation and other digestive problems.
Furthermore, protein metabolism produces many nitrogen byproducts, such as urea and ammonia. These substances require water for the kidneys to excrete. If you don't drink enough water, your body can easily become dehydrated, and your kidneys have to work harder.
Unintentional weight gain
Protein is often considered beneficial for weight loss because it promotes satiety and increases calorie expenditure during digestion. However, when overall calorie intake exceeds needs, any excess calories, even from protein-rich foods, are converted into stored fat.
Risk of nutritional imbalance
Prioritizing protein intake excessively can not only easily lead to deficiencies in fiber, vitamins, and essential minerals, but also negatively impact immunity, gut health, and the microbiome.
Furthermore, if the primary source of protein is animal-derived, and protein-fortified milk contains additives, sugar, and preservatives, it can lead to inflammatory reactions and negatively impact long-term health.
To minimize the harmful effects of excessive protein intake, experts recommend calculating protein intake based on body weight, training intensity, and goals such as muscle gain, fat loss, or maintenance. Gym-goers should also prioritize quality protein sources, alternating between animal and plant-based proteins. Importantly, they should drink enough water, eat enough fiber, and diversify their diet, according to Eating Well .
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/5-tac-hai-khi-nap-qua-nhieu-protein-voi-nguoi-tap-gym-18525092500253677.htm















































































































Comment (0)