The amended Law on Higher Education, recently passed by the 15th National Assembly, has established a legal framework for specialized training in the health sector, including residency and specialist training programs. Based on this, the Ministry of Health is the competent authority to guide, organize, and manage these training programs in accordance with the law.
In practice, both residency and specialist training programs are considered important postgraduate training pathways, contributing to improving the quality of the healthcare workforce. However, these two training methods differ significantly in terms of admission criteria, training timing, and professional development orientation. Clarifying these differences not only helps students choose the appropriate path but is also crucial for planning and developing a highly specialized medical workforce for the healthcare system.
Resident physician - Advanced training immediately after graduation.
Medical residency is a specialized, in-depth training program in the healthcare field, organized for doctors who have graduated from a regular university program. The goal of the program is to train a team of doctors with a solid scientific foundation, systematic specialized knowledge, and advanced clinical practice skills, meeting the requirements for high-quality medical examination and treatment.

Doctors are applying for the 50th residency program at Hanoi Medical University.
According to the regulations and guidelines of the Ministry of Health, residency training is conducted at designated medical training institutions, with a rigorous and highly competitive admission process. Applicants are primarily recent university graduates in medicine with above-average academic results, good moral character, and sufficient health to pursue long-term study and work in the field.
In practice, many training institutions stipulate appropriate graduation timeframes and age requirements to ensure the goal of identifying and nurturing a team of young doctors with long-term professional development potential. Resident doctors are usually trained full-time in a combined hospital and university environment, closely linking academic training with clinical practice, thereby contributing to the formation of a highly specialized medical team for the healthcare system.
Specialist Doctor - Developed on a foundation of professional experience
Unlike residency programs, specialist training (Specialist Level I and Specialist Level II) targets doctors who are already involved in medical examination and treatment within the healthcare system. According to current regulations of the Ministry of Health on postgraduate training in the health sector, this training path aims to improve professional skills based on practical experience and professional practice.
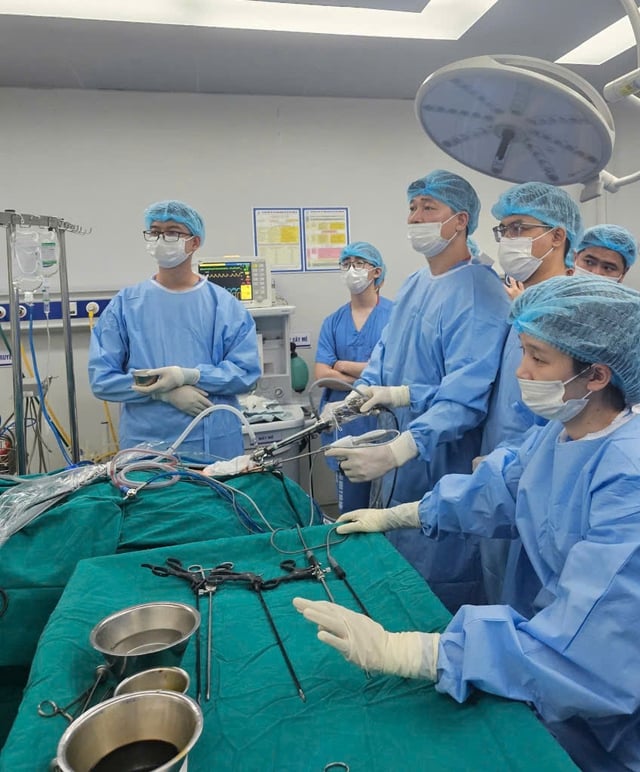
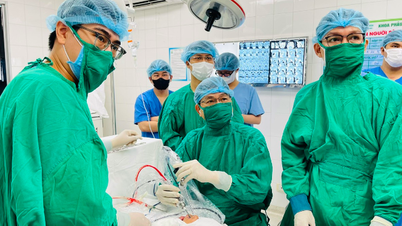
Resident doctors and specialists participate in practice and professional training in a clinical environment.
The eligibility requirements for specialist doctor level (Level I) programs are usually linked to the field of study at the university level. For certain fields as stipulated by the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment, candidates must possess a professional practice certificate. If registering for a specialized training program different from the scope of practice stated in their professional practice certificate, candidates must meet the requirements regarding practical work experience in the registered specialty as guided by the Ministry of Health.
For specialist doctor training (Level II), candidates must have a Level I specialist diploma or a master's degree relevant to the field and specialization they are applying for. In addition, they must meet requirements regarding work experience, professional practice experience, and professional licenses as stipulated by regulations. This roadmap clearly demonstrates the orientation towards training medical experts based on the accumulation of long-term practical experience.
Two pathways, one goal for developing healthcare human resources.
It is clear that both residency and specialist training programs are valuable postgraduate training programs that play a crucial role in improving the quality of the healthcare workforce. Residency programs are intensive training pathways implemented early after university graduation, focusing on identifying and nurturing young doctors with strong academic and practical abilities. Meanwhile, specialist training programs are a professional development path linked to the practice of medicine and the accumulation of practical experience.
Maintaining these two forms of training in parallel contributes to diversifying the career development paths of doctors, while ensuring the continuous succession and development of a highly qualified medical professional workforce, meeting the requirements for caring for, protecting, and improving the health of the people.
Source: https://suckhoedoisong.vn/bac-si-noi-tru-va-bac-si-chuyen-khoa-khac-nhau-nhu-the-nao-169251214222031954.htm















































































































Comment (0)