1. The role of nutrition in liver health
- 1. The role of nutrition in liver health
- 2. Foods that are good for the liver
- 2.1. Coffee – a drink that is good for the liver
- 2.2. Green tea – reduces liver enzymes and fights inflammation
- 2.3. Grapefruit – a source of antioxidants that protect liver cells
- 2.4. Blueberries and cranberries – reduce fatty liver accumulation
- 2.5. Grapes – rich in liver-beneficial plant compounds
- 2.6. Beetroot juice – increases blood flow, reduces inflammation
- 2.7. Cruciferous vegetables – support detoxification and reduce the risk of liver damage
- 2.8. Nuts – support liver enzymes and reduce inflammation
- 2.9. Fatty fish – a source of omega-3 that reduces fatty liver
- 2.10. Olive oil – reduces fat accumulation and improves liver enzymes
- 3. Why are these foods good for the liver?
The liver performs a number of important functions, including the production of cholesterol, bile, and proteins; the storage of vitamins, minerals, and carbohydrates; and the breakdown of toxins from alcohol, medications, and metabolic byproducts. When the liver is under prolonged stress, inflammation, fat accumulation, and oxidative damage can easily occur.
A diet rich in antioxidants, fiber, healthy fats, and cell-protective compounds can help reduce inflammation, aid detoxification, limit fat accumulation, and improve liver enzymes.
2. Foods that are good for the liver
Below are 10 foods that are beneficial for protecting the liver, reducing fat and improving liver function:
2.1. Coffee – a drink that is good for the liver
Information posted on the Toi page said that coffee is considered one of the drinks that are beneficial for the liver. Many studies have shown that drinking coffee regularly helps reduce the risk of chronic liver disease, cirrhosis and liver cancer. Drinking about three cups of coffee a day brings the most obvious effect.
Coffee works by:
- Prevents fat and collagen accumulation – two factors that promote liver damage
- Increases levels of glutathione, the body's master antioxidant
- Reduce oxidative stress and protect liver cells...
Thanks to that, coffee becomes a powerful liver-supporting food when used in moderation (note that black coffee does not contain added sugar, milk, etc.).
2.2. Green tea – reduces liver enzymes and fights inflammation
Green tea contains many polyphenols that help improve liver function. Clinical analysis shows:
- Regular green tea consumption may reduce liver enzymes in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- People who drink several cups of tea a day have a lower risk of liver cancer.
However, users should avoid overusing concentrated green tea extract, as there have been rare cases of liver damage. The safest way is still to drink regular brewed green tea.
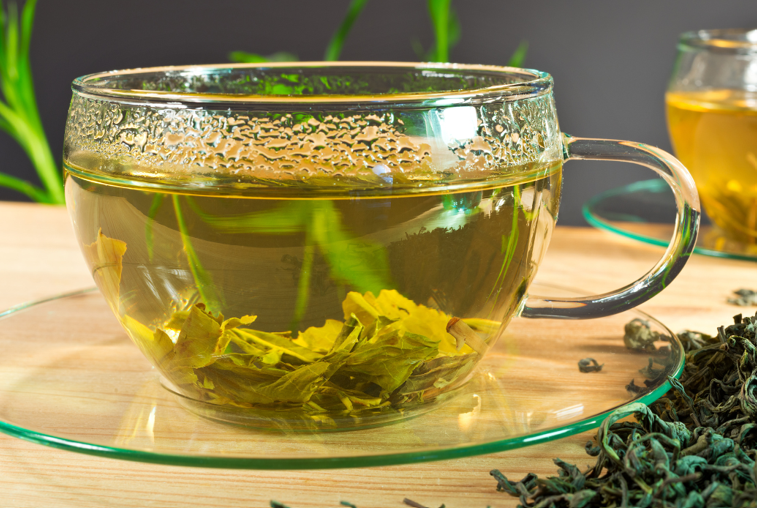

Green tea contains polyphenols that help improve liver function.
2.3. Grapefruit – a source of antioxidants that protect liver cells
Grapefruit is rich in naringin and naringenin, two antioxidants that help:
- Reduce inflammation
- Protect liver cells
- Slows the progression of liver fibrosis in animal studies.
Although much of the data is based on animal models, current evidence suggests that grapefruit may contribute to reducing liver damage and oxidative stress when added to the daily diet.
2.4. Blueberries and cranberries – reduce fatty liver accumulation
Blueberries and cranberries contain anthocyanins, powerful antioxidants that help:
- Reduce fat accumulation in the liver
- Improves signs of fatty liver.
Cranberry supplements have been shown to improve NAFLD in some studies. Blueberry extract may inhibit the growth of liver cancer cells in a lab setting. Adding berries to your diet is an easy way to increase your natural source of antioxidants.
2. 5. Grapes – rich in liver-healthy plant compounds
Red and purple grapes are rich sources of plant antioxidants. Animal studies show that grapes may:
- Reduce inflammation
- Reduce liver cell damage
- Increase antioxidant capacity.
Although human studies have been inconsistent, grapes are a nutritious food. Eating whole grapes is recommended over taking grape seed extract.
2. 6. Beetroot juice – increases blood flow, reduces inflammation
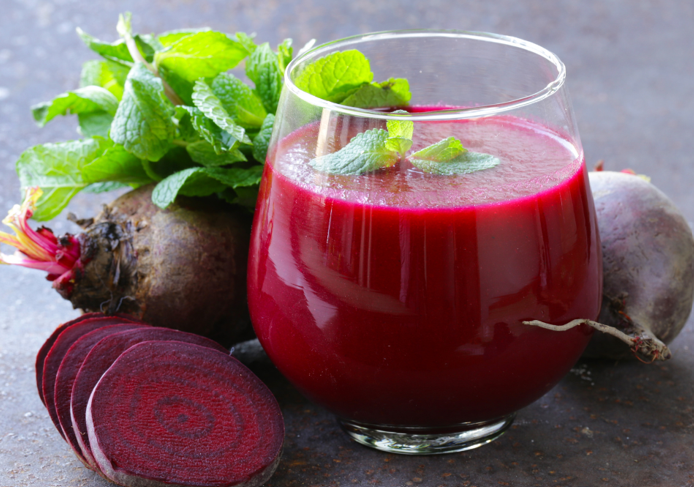

Beetroot juice may reduce oxidative damage in the liver and provide long-term protective benefits.
Beetroot juice contains:
- Natural nitrates
- Betalain – powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory.
Animal studies have shown that beetroot juice can reduce oxidative damage in the liver and provide long-term protective benefits. Although human studies are limited, the nutrient-rich drink may help support blood flow and reduce inflammation, which indirectly benefits the liver.
2. 7. Cruciferous vegetables – support detoxification and reduce the risk of liver damage
Cruciferous vegetables include: Broccoli, kale, cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts... These vegetables are rich in fiber and plant compounds that support the liver detoxification process.
Studies show they help:
- Neutralize toxic chemicals
- Reduce the risk of liver damage
- Reduced fat accumulation and decreased the number of liver tumors in animal studies...
Although more human data are needed, cruciferous vegetables remain an essential food group in a liver-healthy diet.
2. 8. Nuts – support liver enzymes and reduce inflammation
Nuts contain healthy fats, vitamin E, antioxidants, bioactive compounds… These components help improve metabolism and reduce inflammation – key factors in protecting the liver. Some studies show that a diet rich in nuts helps reduce the risk of NAFLD. This is a food group that should be present in the daily diet.
2.9. Fatty fish – a source of omega-3 that reduces fatty liver
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are well-known sources of omega-3s, which have been shown to reduce liver fat, triglycerides, and improve liver markers in people with NAFLD.
The omega-3/omega-6 ratio is also important. Reducing foods high in omega-6 (such as frying oils) and increasing omega-3 helps reduce inflammation, which contributes to liver damage.
2. 10. Olive oil – reduces fat accumulation and improves liver enzymes
Olive oil is a staple of the Mediterranean diet. Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants. Research shows that olive oil can reduce fat accumulation in the liver, improve liver enzyme levels, and support metabolism and heart health. Consuming olive oil can help prevent the early stages of fatty liver disease.
3. Why are these foods good for the liver?
Foods that are good for the liver are often rich in:
1. Antioxidants: Help reduce oxidative stress – the leading cause of liver damage.
2. Fiber: Supports weight control, improves detoxification and reduces the risk of fatty liver.
3. Healthy fats and high-quality proteins: Help regulate blood sugar, reduce inflammation, and limit insulin resistance – factors closely related to NAFLD and type 2 diabetes.
Adding a variety of the above foods to your daily diet is one of the simplest ways to protect your liver long-term.
Maintaining liver health is not just a matter for those with risk factors or diagnosed with liver disease, but a priority for everyone. The liver works continuously every day to process toxins, metabolize energy and protect the body, so diet plays a particularly important role in reducing the burden on this organ.
Including foods rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and cell-protective compounds—like coffee, green tea, cruciferous vegetables, and fatty fish—in your diet regularly can help limit fat accumulation, reduce inflammation, and improve liver function over time.
However, nutrition is only one part of a comprehensive liver care strategy. Limiting alcohol, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and having regular health check-ups are all integral factors. Combining a healthy lifestyle with the right food choices will help you protect your liver effectively, thereby supporting your overall health and long-term quality of life.
Readers are invited to see more:
Source: https://suckhoedoisong.vn/10-thuc-pham-giup-duong-gan-thanh-nhiet-va-giam-tich-tu-mo-169251206185704749.htm





![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives the Director of the Academy of Public Administration and National Economy under the President of the Russian Federation](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F08%2F1765200203892_a1-bnd-0933-4198-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)





































































































Comment (0)